3 myths about neurodermatitis
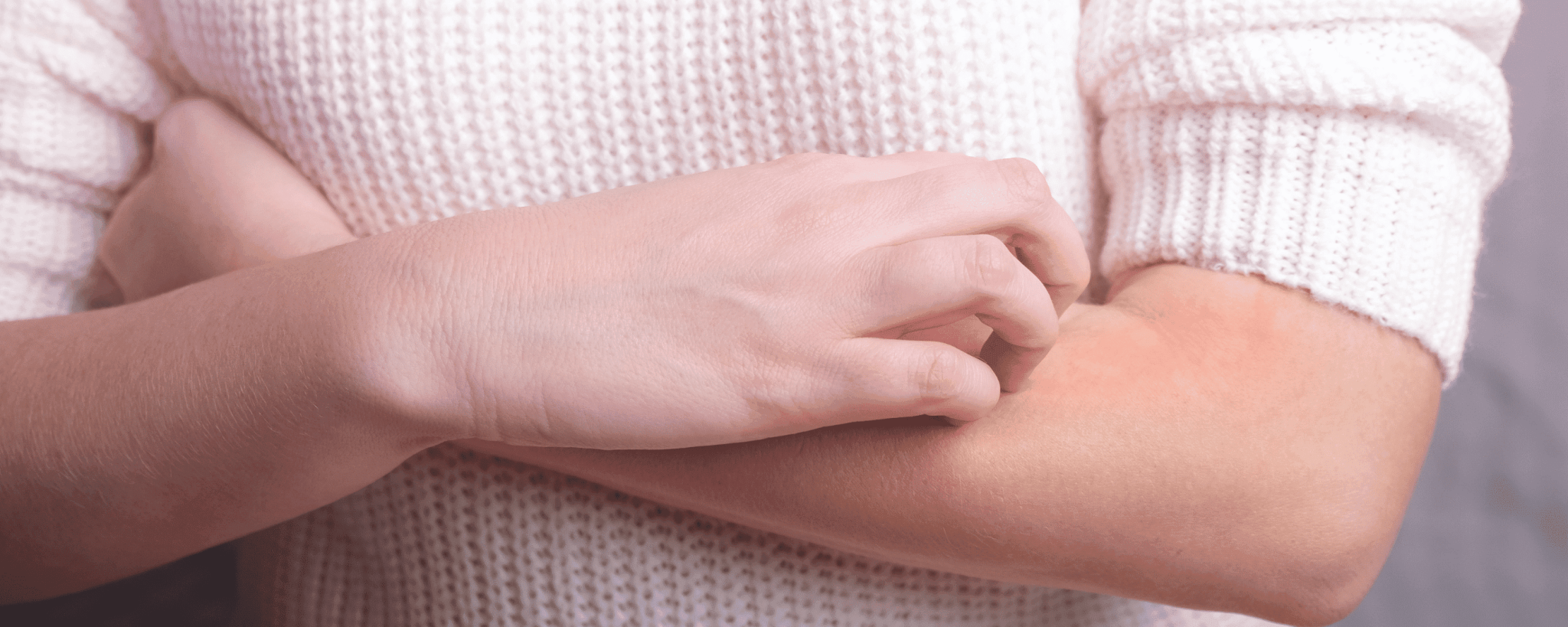

Neurodermatitis is one of the most common chronic skin diseases in Germany. The disease manifests itself in red, itchy and scaly skin changes that occur primarily on the flexural sides of the joints, on the face and on the neck. Unfortunately, neurodermatitis is often still associated with stigma. Many people know too little about the causes and symptoms of the disease.
Today we would like to clear up 3 widespread myths about neurodermatitis.
What is neurodermatitis?
Occurrence in Germany
Neurodermatitis, also known as atopic dermatitis , is one of the most common chronic skin diseases in Germany. It is estimated that around 4 to 6 million people in this country are affected by neurodermatitis - that corresponds to around 5-8% of the population. Neurodermatitis can occur at any age, but most frequently in childhood.
This is how neurodermatitis manifests itself
The disease manifests itself in red, itchy and scaly skin changes. These symptoms typically appear mainly on the joints, face and neck. Other parts of the body can also be affected. The severe itching that accompanies neurodermatitis often leads to scratching and rubbing, which in turn increases the skin inflammation.
Trigger for neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis attacks are often triggered by environmental factors such as stress, sweating, certain foods or allergens. Individual genetic predispositions also play a role. In people with neurodermatitis, the immune system reacts much more sensitively to various stimuli, which leads to inflammatory reactions in the skin.
Effects on well-being
Many sufferers find their neurodermatitis a great burden, not only physically but also psychologically. Due to the sometimes very visible symptoms, they often feel stigmatized and excluded. This makes it all the more important to break down misconceptions about the causes and treatment options for the disease.
Myth #1: Neurodermatitis is a purely psychological illness
Wrong. The causes of neurodermatitis are multifactorial. In addition to genetic factors, environmental influences and immune reactions also play an important role. Psychological factors can intensify symptoms, but they are not the sole cause of the disease. Neurodermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that requires medical treatment.
Myth #2: Neurodermatitis is contagious
Wrong. Neurodermatitis is not a contagious disease. It cannot be transmitted from person to person. The skin changes are caused by over-excitable skin and inflammatory reactions, not by bacteria or viruses. Therefore, there is no risk of infection for other people.
Myth #3: Neurodermatitis cannot be treated
Wrong. There are certainly effective treatment options for neurodermatitis. Through consistent skincare, the use of anti-inflammatory creams and, if necessary, medication, the symptoms can be significantly alleviated in most cases. The aim of therapy is to reduce inflammation, relieve itching and stabilize the skin barrier. With the right treatment, those affected can significantly improve their quality of life.
Conclusion - the myths about neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis is a widespread disease, but one that is often still associated with prejudice. By educating people and sharing well-founded information, we can help to break down misconceptions. Neurodermatitis is not a purely psychological or contagious disease and can be treated - that is the reality that we want to convey.
For people with sensitive skin and scalp that is prone to irritation, natüür offers a range of specially developed care products that are based in particular on N EEMAVERA and coconut. Together, these high-quality natural cosmetics from natüür form an effective care system that can help those affected by neurodermatitis to soothe their skin and restore a feeling of well-being.